Benchmarking: A Key Tool in Your Arsenal
Professional sports teams do it. Heads of industry do it. Even governments do it. We’re talking about benchmarking, or the practice of comparing your performance against similar peers and competitors to gauge where you need to improve. As Peter Drucker said, “Being at least as good as the leader is a prerequisite to being competitive”.
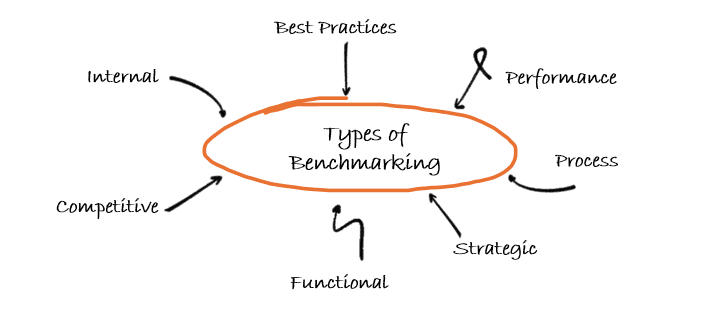
So, what exactly is involved in benchmarking, and how do you go about the process of comparing yourself to others? The fundamental steps are as follows:
- Define the type of benchmarking. There are many types of benchmarking studies. Start by defining either an internal or external benchmark study. An internal, functional benchmark is helpful for drafting performance or process “best practices”. If you’re looking to compare your company’s products or services with a competitor’s, you may consider a strategic benchmarking study focusing on long-term targets (think 5+ years) that follow a linear path towards “best-in-class” metrics. Alternatively, a competitive benchmark can be used to analyze why your rival is getting better customer feedback and outline specific steps to improve the quality of your product or service.
- Identify what to benchmark. Are you looking to improve a specific KPI, such as the customer’s satisfaction index or the service call waiting time? You will need to select the service or product metric that needs improvement. Just keep in mind that a benchmark is a way to reference relative performance, whereas a KPI is the measurement of performance towards a specific goal.
- Decide on the standard and collect the data. Collecting data from a direct competitor might be difficult (or illegal) to obtain, which is why it’s useful to use industry group data in order to gather information from several sources to get neutral information from several organizations. Internal data is easier to gather, but you might run into improvement limitations if the peer group is not considered “world class”. This can be done with primary information through surveys, personal research, interviews, public data, industry group publications. You can also collect secondary information from company websites, on-line reports, marketing materials, or news articles.
- Measure performance & Analyze the data. This step starts with developing a data collection plan, completing a measurement system analysis, and finalizing the project data collection plan. The team will gather the data that is used to baseline performance. Next, you will determine how capable your process is of producing defect-free products or services. The objective is to analyze the data for trends, patterns, and outliers to understand where your business is leading or lagging. It’s important to identify why there are gaps in your process. For example, are your representatives sufficiently trained to provide above and beyond service? Perhaps there is a new automated technology that a competitor is using to cut down on wait times. This is where you will want to perform a root cause analysis, which will then feed into a brainstorm of ideas to fill in the gaps.
- Implement solutions. This is the fun part! Make sure the team is on-board with what specific changes need to be made to directly address a root cause. Be creative. Take calculated risks. Just be sure to consider any unintended consequences of the solutions so that you don’t inadvertently cause a new problem. You will need to monitor the changes for effectiveness. Check the KPI for performance gains. If the new process is not running as expected, then go back and re-tweak.
- Have a control plan in place. Once the new ideas have been implemented, be sure to have a solid control plan in place outlining who will be responsible for monitoring and taking action if the new process starts to slip backwards again.
The goal of any business is to remain competitive, viable and financially stable. Benchmarking is a key tool that can help you stay ahead, or at least run with the pack. It’s part of any continuous improvement program within your organization.
